CMI researchers from Ames National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
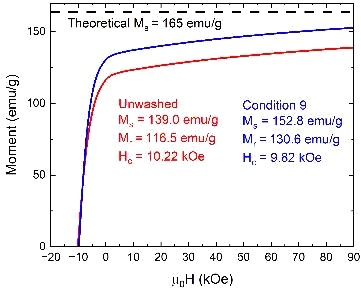
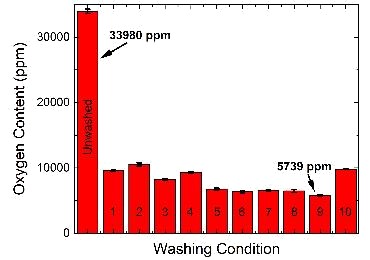
Optimized the post-synthesis washing procedure of Sm2Fe17N3 powders crucial to enhancing magnetic properties of the dense magnets.
Achievement
Achieved ~5X reduction in oxygen content for Sm2Fe17N3 powders.
Significance and Impact
Synthesis of Sm2Fe17N3 via reduction-diffusion of Sm2O3 leads to the formation of CaO as side product. Removing CaO without introducing undesirable surface oxidation leads to degradation of magnetic performance during consolidation. New solvents and washing condition resulted in our lowest measured oxygen content yet and yield sustainable, scabble process.
Hub Target Addressed
Increasing the speed of discovery and integration.